Table of Contents
EQ1979 Analog Console Strip

EQ1979 is a stereo VST analog console strip emulation inspired by a famous British console module with red gain knob. UI design by Fluidshell

EQ1979 has three stages:
- Input Driving stage, which emulates a transformer based analog input amplifier with smooth saturation.
- Filtering stage with low shelf, mid band, and high shelf inductor-based filter emulation
- A Third order highpass filter emulation
Support by email : vince[]bellesondes.fr
Download
Version 1.02 - 11/08/2023
Changelog:
- 1.02 Bugfixes and user feedback implementation
- Fixed a bug on High Shelf response stereo diffrerence,
- Added a control to passivate internal electronics noise simulation to avoid noise stacking on projects with multiple instances involved
- Anti-aliasing filter frequency tied to 0.48x sampling frequency to allow projects with greater sample rate to take benefit from a broader high frequency range.
- Added control readouts for Drive and Gains controls
- Added mouseover hints on every control
- 1.01 Fixed pairing stereo outputs
- 1.0 Initial (Release Candidate)
Access previous versions - Ongoing Beta Stream
Support, Feedback, and kind words are welcome by email | fediverse
If you like EQ1979, you can tip 1.979 and 
Installation
- Windows : Extract archive to your VST3 folder (default c:\program files\common files\VST3)
- Mac : Copy the entire EQ1979.component folder to your Mac folder /Library/Audio/Plug-Ins/Components/
Troubleshooting:
- Note that the Library folder on a Mac is a hidden folder. More information: https://www.macworld.com/article/2057221/how-to-view-the-library-folder-in-mavericks.html
User Guide
Input driving stage
- Drive : [0.1 to 100](%) input driving factor. Use it to add saturation ranging from smooth harmonics to harsh console driving.
- Trim : [-24 to 24](dB) drive output gain trimming in 1dB steps. Use it to trim input stage signal level before hitting filter stage. Designed as a simple multiplicative gain.
- OS (oversampling) : Applies oversampling to saturation stage to avoid high frequency harshness.
Input stage was modeled to mimic the behavior of a dual BA284 input module with smooth frequency bumps from transformer stage. Saturation has smooth 3rd ans 5th harmonics content, with additional harmonic content above 2/3 of saturation control dialed in. It has an internal 1:2 embedded gain compensation when set at 10.
Oversampling provides better sound quality at the expense of performance. “x” ratio is calculated with regards to a 48kish sampling frequency (e.g. applying 2x Oversampling when using 96kHz project frequency has no impact).
EQ and Phase
- EQ: [On,Off] Enables or disables the EQ stage,
- Phase: [On, Off] Inverts signal phase,
When enabled, EQ slightly changes frequency response, just like in original channel strips when BAxxx modules from filter are enabled.
High Shelf Filter
- Level: [-16:0:+16](dB) high shelf filter gain.
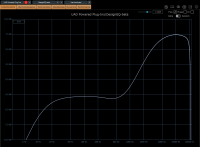
High shelf filter is a 9.3kHz centered high shelf filter. It mimics the frequency response of the original analog module in that it is broad, with that typical 440Hz drop coupled to filter gain as in original inductive filter design.
This gives the unit its typical “air” sound which sounds great with a bit of input saturation.
Medium Band Shelf
Controls:
- Level : [-18:0:+18](dB) gain at selected frequency,
- Frequency : [Off, 360<>7200 Hz] use it to select the bell curve frequency,
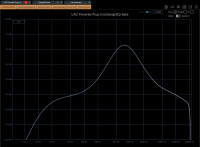
Mid band provides this typical large bell curve from the original console strip, while emulating its electrical influence on input signal when enabled.
Six band are available as per design : 360Hz, 700Hz, 1.6kHz, 3.2kHz, 4.8kHz, 7.2kHz.
Low Shelf
Controls:
- Level : [-16:0:+16](dB) low shelf filter gain.
- Frequency : [Off, 35<>220](Hz) use it to select the bell curve frequency,
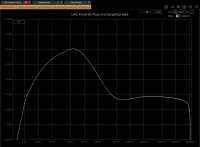
Low shelf is a multi frequency shelving filter emulating analog inductive shelving circuitry. Hence, it has this typical smooth bump above the selected frequency. ~
Selected frequency ranges from 35, 60, 110 and 220Hz. Each setting has different “null” frequency response, because of inner eletrical design emulation of the original circuitry.
Highpass filter

Controls :
- Frequency: [50<>300](Hz) frequency control,
Highpass filter is a 3rd order capacitive filter with selectable frequency designed as per original console strip frequency response.
Technology
Input saturation uses a subtle combination of arctangent and polynomial math to first boost 3rd and 5th harmonics while increasingly switching to a full spectrum asymetrical saturation. Loudness partial compensation is linear.
Filtering uses a combination of more than 50 butterworth maximally flat one pole filters to frequency match the existing console strip behavior. A fine-tuned parametric model dynamically parameters those filters upon console strip inputs.
Modeling accurately the lectronics implied adding several asymetrical bias, noise sources and non linearities which tend to reproduce the unique analog console sound.
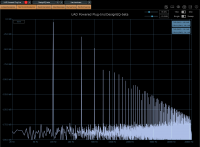
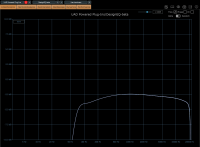
Part of modeling that real console behavior, even filter idle states trigger frequency response variations, as shown here
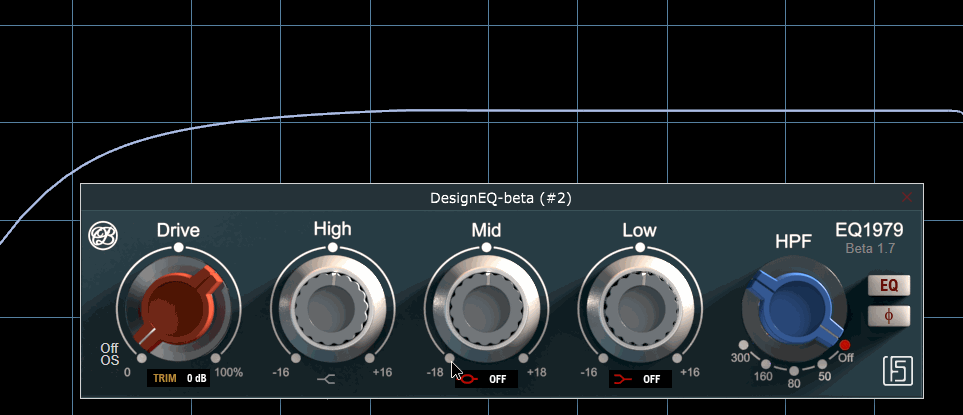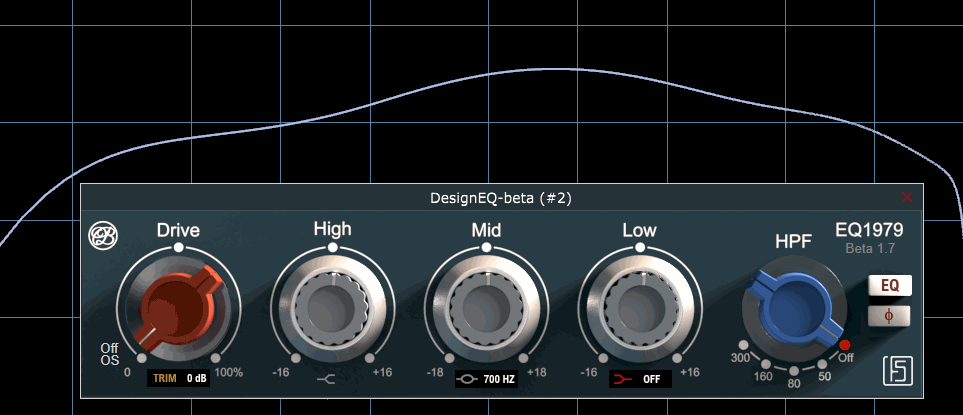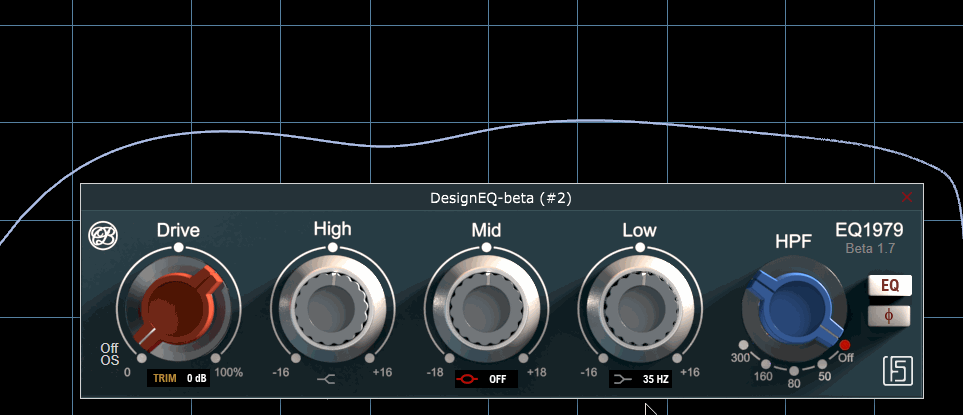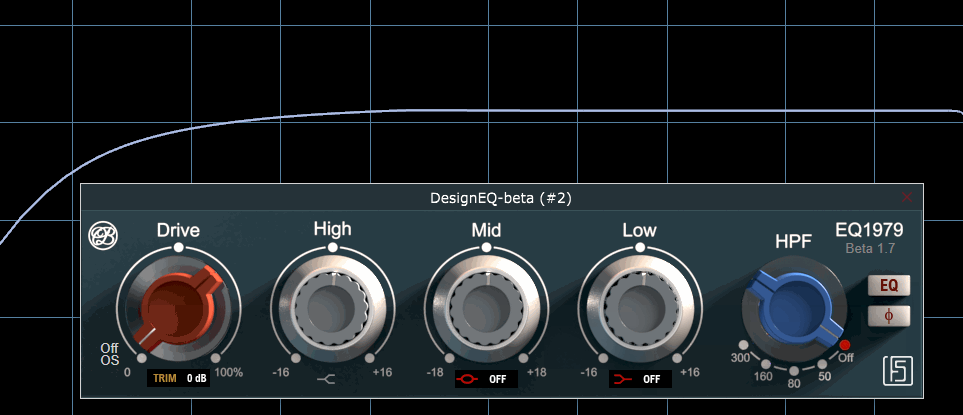
GUI gracefully designed by Steph from https://www.fluidshell.com. Visit his website for top-notch hardware and software GUI design.
Belles Ondes material released under Steinberg VST3 License V3.7.6
VST is a registered trademark of Steinberg Technologies GmbH
VST EQ1979 Analog Strip and EQ (Beta Stream)
Access for Beta versions is closed. Thanks for the help guys, enjoy release!